
关于并查集的一切
并查集初识
如果给你一些顶点,并且告诉你每个顶点的连接关系,你如何才能快速的找出两个顶点是否具有连通性呢?如「图 5. 连通性问题」,该图给出了顶点与顶点之间的连接关系,那么,我们如何让计算机快速定位 (0, 3) , (1, 5), (7, 8) 是否相连呢?此时我们就需要机智的「并查集」数据结构了。很多地方也会称「并查集」为算法,这也没问题。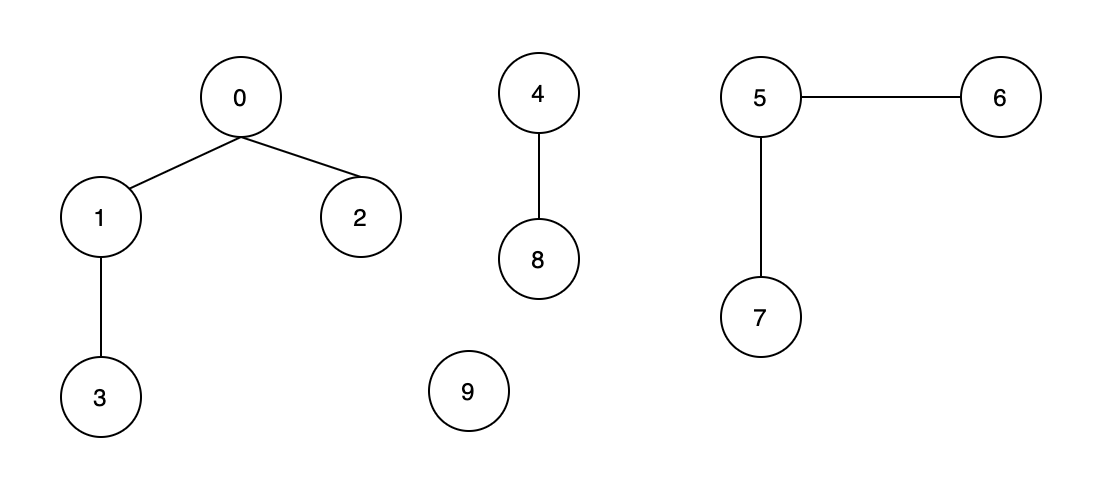 「并查集」的主要作用是用来解决网络中的连通性。这里的「网络」可以是计算机的网络,也可以是人际关系的网络等等。例如,你可以通过「并查集」来判定两个人是否来自同一个祖先。
「并查集」的主要作用是用来解决网络中的连通性。这里的「网络」可以是计算机的网络,也可以是人际关系的网络等等。例如,你可以通过「并查集」来判定两个人是否来自同一个祖先。
「并查集」常用术语
- 父节点:顶点的直接父亲节点。如「图5. 连通性问题」中,顶点 3 的父节点是 1;顶点 2 的父节点是 0;顶点 9 的父节点是自己本身 9。
- 根节点:没有父节点的节点,本身可以视为自己的父节点。如「图5. 连通性问题」中,顶点 3 和 2 的根节点都是 0;0 即是自己本身的父节点,也是自己的根节点;顶点 9 的根节点是自己本身 9。
「并查集」基本思想
视频内容摘要:
- 如何在计算机中设计出「并查集」数据结构
- 「并查集」的
find函数; - 「并查集」的
union函数。
「并查集」的两个实现方式
- Quick Find 实现方式:它指的是实现「并查集」时,find 函数时间复杂度很低为 O(1)O(1),但对应的 union 函数就需要承担更多的责任,它的时间复杂度为 O(N)O(N)。
- Quick Union 实现方式:它指的是实现「并查集」时,相对于 Quick Find 的实现方式,我们通过降低 union 函数的职责来提高它的效率,但同时,我们也增加了 find 函数的职责。
Quick Find 方式实现并查集
Quick Find工作原理:
代码实现与验证
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class UnionFind{
private:
int* root;
int length;
public:
UnionFind(int size):length(size){
root = new int[size];
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
root[i] = i;
}
}
int find(int x){
return root[x];
}
void merge(int x,int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if(rootX!=rootY){
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
if(root[i]==rootY)
root[i] = rootX;
}
}
}
bool isconnected(int x,int y){
return find(x)==find(y);
}
};
int main(){
UnionFind a(10);
a.merge(1,2);
a.merge(2,5);
a.merge(5,6);
a.merge(6,7);
a.merge(3,8);
a.merge(8,9);
cout<<a.isconnected(1,5)<<' '<<a.isconnected(5,7)<<' ';
cout<<a.isconnected(4,9)<<' ';
a.merge(9,4);
cout<<a.isconnected(4,9);
}
时间复杂度
| UnionFind 构造函数 | find 函数 | merge函数 | isconnected 函数 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 时间复杂度 | O(N) | O(1) | O(N) | O(1) |
注:N 为「图」中顶点的个数。
Quick Union 方式实现并查集
Quick Union的工作原理
为什么 Quick Union 比 Quick Find 更加高效?
总体来说,Quick Union 是比 Quick Find 更加高效的。为什么呢?
代码实现与验证
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class UnionFind{
private:
int* root;
int length;
public:
UnionFind(int size):length(size){
root = new int[size];
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
root[i] = i;
}
}
int find(int x){
while(x!=root[x]){
x = root[x];
}
return x;
}
void merge(int x,int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if(rootX!=rootY){
root[rootY] = rootX;
}
}
bool isconnected(int x,int y){
return find(x)==find(y);
}
};
int main(){
UnionFind a(10);
a.merge(1,2);
a.merge(2,5);
a.merge(5,6);
a.merge(6,7);
a.merge(3,8);
a.merge(8,9);
cout<<a.isconnected(1,5)<<' '<<a.isconnected(5,7)<<' ';
cout<<a.isconnected(4,9)<<' ';
a.merge(9,4);
cout<<a.isconnected(4,9);
}
时间复杂度
| UnionFind 构造函数 | find 函数 | merge函数 | isconnected 函数 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 时间复杂度 | O(N) | O(H) | O(H) | O(H) |
注:N 为「图」中顶点的个数,H 为「树」的高度。
按秩合并优化并查集
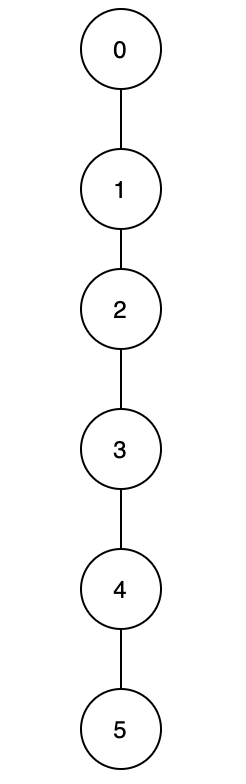
小伙伴看到这里的时候,我们其实已经实现了 2 种「并查集」。但它们都有一个很大的缺点,这个缺点就是通过 merge 函数连接顶点之后,可能所有顶点连成一条线形成「图 5. 一条线的图」,这就是我们 find 函数在最坏的情况下的样子。那么我们有办法解决吗?
当然,伟大的科学家已经给出了解决方案,就是按秩合并。这里的「秩」可以理解为「秩序」。之前我们在 merge 的时候,我们是随机选择 x 和 y 中的一个根节点/父节点作为另一个顶点的根节点。但是在「按秩合并」中,我们是按照「某种秩序」选择一个父节点。
这里的「秩」指的是每个顶点所处的高度。我们每次 merge 两个顶点的时候,选择根节点的时候不是随机的选择某个顶点的根节点,而是将「秩」大的那个根节点作为两个顶点的根节点,换句话说,我们将低的树合并到高的树之下,将高的树的根节点作为两个顶点的根节点。这样,我们就避免了所有的顶点连成一条线,这就是按秩合并优化的「并查集」。
视频讲解
代码实现与验证
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class UnionFind{
private:
int* root;
int* rank;
int length;
public:
UnionFind(int size):length(size){
root = new int[size];
rank = new int[size];
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
root[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
int find(int x){
while(x!=root[x]){
x = root[x];
}
return x;
}
void merge(int x,int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
//高度小的树被高度大的合并,如果高度一致合并后高度增加
if(rootX!=rootY){
if(rank[rootX]>rank[rootY]){
root[rootY] = rootX;
} else if(rank[rootX]<rank[rootY]){
root[rootX] = rootY;
}else{
root[rootY] = rootX;
rank[rootX]++;
}
}
}
bool isconnected(int x,int y){
return find(x)==find(y);
}
};
int main(){
UnionFind a(10);
a.merge(1,2);
a.merge(2,5);
a.merge(5,6);
a.merge(6,7);
a.merge(3,8);
a.merge(8,9);
cout<<a.isconnected(1,5)<<' '<<a.isconnected(5,7)<<' ';
cout<<a.isconnected(4,9)<<' ';
a.merge(9,4);
cout<<a.isconnected(4,9);
}
| UnionFind 构造函数 | find 函数 | merge函数 | isconnected 函数 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 时间复杂度 | O(N) | O(logN) | O(logN) | O(logN) |
注:N 为「图」中顶点的个数。
路径压缩优化的并查集
从前面的「并查集」实现方式中,我们不难看出,要想找到一个元素的根节点,需要沿着它的父亲节点的足迹一直遍历下去,直到找到它的根节点为止。如果下次再查找同一个元素的根节点,我们还是要做相同的操作。那我们有没有什么办法将它升级优化下呢?
答案是可以的!如果我们在找到根节点之后,将所有遍历过的元素的父节点都改成根节点,那么我们下次再查询到相同元素的时候,我们就仅仅只需要遍历两个元素就可以找到它的根节点了,这是非常高效的实现方式。那么问题来了,我们如何将所有遍历过的元素的父节点都改成根节点呢?这里就要拿出「递归」算法了。这种优化我们称之为「路径压缩」优化,它是对 find 函数的一种优化。
视频讲解
实际路径压缩应该还有一种迭代的方式,此视频未提到。
代码实现(路径压缩+按秩合并)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class UnionFind{
private:
int* root;
// 添加了 rank 数组来记录每个顶点的高度,也就是每个顶点的「秩」
int* rank;
int length;
public:
UnionFind(int size):length(size){
root = new int[size];
rank = new int[size];
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
root[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
int find(int x){
//递归方式
if(x==root[x])
return x;
return root[x]=find(root[x]);
/*迭代方式
int cur = x;
while(cur!=root[cur]){
root[cur] = root[root[cur]];
cur = root[cur];
}
return cur;*/
}
// 按秩合并优化的 merge 函数
void merge(int x,int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
//高度小的树被高度大的合并,如果高度一致合并后高度增加
if(rootX!=rootY){
if(rank[rootX]>rank[rootY]){
root[rootY] = rootX;
} else if(rank[rootX]<rank[rootY]){
root[rootX] = rootY;
}else{
root[rootY] = rootX;
rank[rootX]++;
}
}
}
bool isconnected(int x,int y){
return find(x)==find(y);
}
};
int main(){
UnionFind a(10);
a.merge(1,2);
a.merge(2,5);
a.merge(5,6);
a.merge(6,7);
a.merge(3,8);
a.merge(8,9);
cout<<a.isconnected(1,5)<<' '<<a.isconnected(5,7)<<' ';
cout<<a.isconnected(4,9)<<' ';
a.merge(9,4);
cout<<a.isconnected(4,9);
}
| UnionFind 构造函数 | find 函数 | merge函数 | isconnected 函数 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 时间复杂度 | O(N) | O(⍺(N)) | O(⍺(N)) | O(⍺(N)) |
注:N 为「图」中顶点的个数。
综合运用例题
解题代码
这效率yyds!
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) {
int n = isConnected.size();
root = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
root[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
cnt = n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if(isConnected[i][j])
merge(i,j);
}
}
return cnt;
}
private:
int* root;
int* rank;
int cnt;
int find(int x){
if(root[x] == x)
return x;
return root[x] = find(root[x]);
}
void merge(int x,int y){
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if(rootX!=rootY){
if(rank[rootX]<rank[rootY])
root[rootX] = rootY;
else if(rank[rootX]>rank[rootY])
root[rootY] = rootX;
else{
root[rootX] = rootY;
rank[rootY]++;
}
//初始有多个集合,一旦合并一次就少一个集合
cnt--;
}
}
};

